At the end of last month I had the opportunity to spend a morning at the new textile store for the British Museum in Blyth House, West London. With the patient assistance of curator Julie Hudson and Textile Centre manager Helen Wolfe I was able to look closely at a number of robes and cloths from the British Museum’s vast collection that had attracted my attention either in publications or via their online database. (The entire collection is now online here and provides a hugely important resource for those interested in studying African textiles.)
Although I am lucky enough to spend most of my days surrounded by stacks of old African cloths there is in my view always more to be learned and more details to be grasped by paying close attention to threads, weaves, patterns, constructions, layouts, textures, etcetera. Some of these can be learned from photographs but actually seeing and handling cloths reveals more again. [Any of the cloths, or indeed other items, in the collection of the British Museum can be viewed by appointment and curators are generally happy to help.]
Over the next few weeks I will be writing a short series of posts based on this visit, beginning today with a look at two robes from Sierra Leone or, more probably, Liberia. One of these has been frequently published and the other is very obscure.
My attention was drawn to this simple and rather stained looking robe (British Museum number AF,WA.10) by the early accession number and the brief description on the image page “Embroidered garment made of cloth (grass).” In old descriptions and travellers accounts of West African textiles cloths described as woven of “grass” are generally actually woven from raffia (the dried inner leaves of a type of palm tree. While cloths woven from raffia on the upright single heddle loom in West Africa are reasonably widespread, strip woven raffia cloths are extremely rare (primarily, I think, because raffia thread could only provide short lengths that had to be tied together.)
There is no detailed record surviving of the origin or accession date of the robe but it appears to be part of the collection left to the museum by Henry Christy (1810-1865.) Disappointingly the first thing that became apparent when we handled and examined this robe was that despite the rather harsh scratchy texture, it was in fact woven from hand spun cotton not raffia. Raffia is not spun so on close examination the fibres are flat rather than round as here. [The main description on the BM page has now been corrected following our examination.]
So what accounts for the pale beige colour and harsh texture ? The robe appears to have been soaked in some kind of plant based dye (most probably after robe was tailored but before it was embroidered.) Although I am not aware of any documentation of this practice in the southern part of Sierra Leone or Liberia, it is still in use in the making of “war shirts” called hu ronko among the Limba people in the north of the country and in neighbouring Guinea. In their book Blues et ocres de Guinée Anne-Chantal Gravellini and Annie Ringuedé describe the use of the bark of the tree terminalia ivorensis along with the kola nut Cola nitida to dye cloths and tunics a variety of ochre shades.
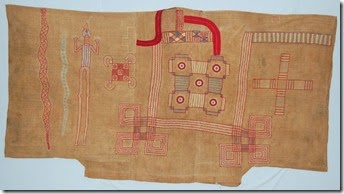
Also notable was the regular placement of thicker wefts at intervals along each strip of cloth. The embroidery, although limited in area and elaboration, is quite complex in design. Below is a detail from the back. Imported wool, cotton and silk is used.
The pocket has the folded over corner and oblique placing that were found on many robes from the Guinea Coast region and help to distinguish them from the better known robes of Mali and Nigeria.
The sides of the robe are completely open but it can be seen that they were once sewn up at the lower part. This sleeveless structure would put this robe within the group that the Lambs (Sierra Leone Weaving by Venice and Alastair Lamb) report are called kusaibi, while the second robe that we looked at, with a more complex tailored design is called in Manding duriki ba.
Below we show front and back views from the BM site (BM accession number Af1934,0307.218). This robe was part of the Beving collection accessioned in 1934 but can be assumed to be from the nineteenth century.
Published by the Lambs with photographs that make it look very yellow this remarkable robe is in fact a very similar pale ochre colour to the first one we looked at, although it is softer to handle.
In this robe also there is a decorative effect in the cloth used achieved by adding thicker threads in the weft, albeit here in blocks rather than the single threads used in Af.WA.10. This is a quite unusual technique in West African strip weaving and may in itself point towards an origin in the same region. In his book Le Boubou –c’est chic (Basel, 2000), Bernhard Gardi attributes the very small number of robes of this type to Liberia. A blue ground robe with rather similar embroidery to this was collected in 1932 from a Mano chief in a village called Blaui in northern Liberia.
Click on the photos to enlarge. In the post above all detail photos are by Duncan Clarke and the full views are from the linked pages on the British Museum site.











thank you for this awesome venue!!!
ReplyDeleteDuncan, is that amazing figure ON STILTS? It certainly seems to be, and certainly there are Dan stiltdancers in the region. Remarkably naturalistic head to body proportions, too (not counting the stilts)
ReplyDelete